Note on Final Projects Be aware this is coming. Start thinking about who you will like to work with and what you will want to do. Here are some general remarks.
You might want to play with JavaFX. Yep, it's fun and very cool and you can
create GUIs. You can install it on your machine by going to the Java Resources
Page and there are directions for installing and for ensuring you have done so
correctly. You can view the API Guide for it.
Students in 4280 are familiar with it. Here is a window generated
by HelloFX.java.
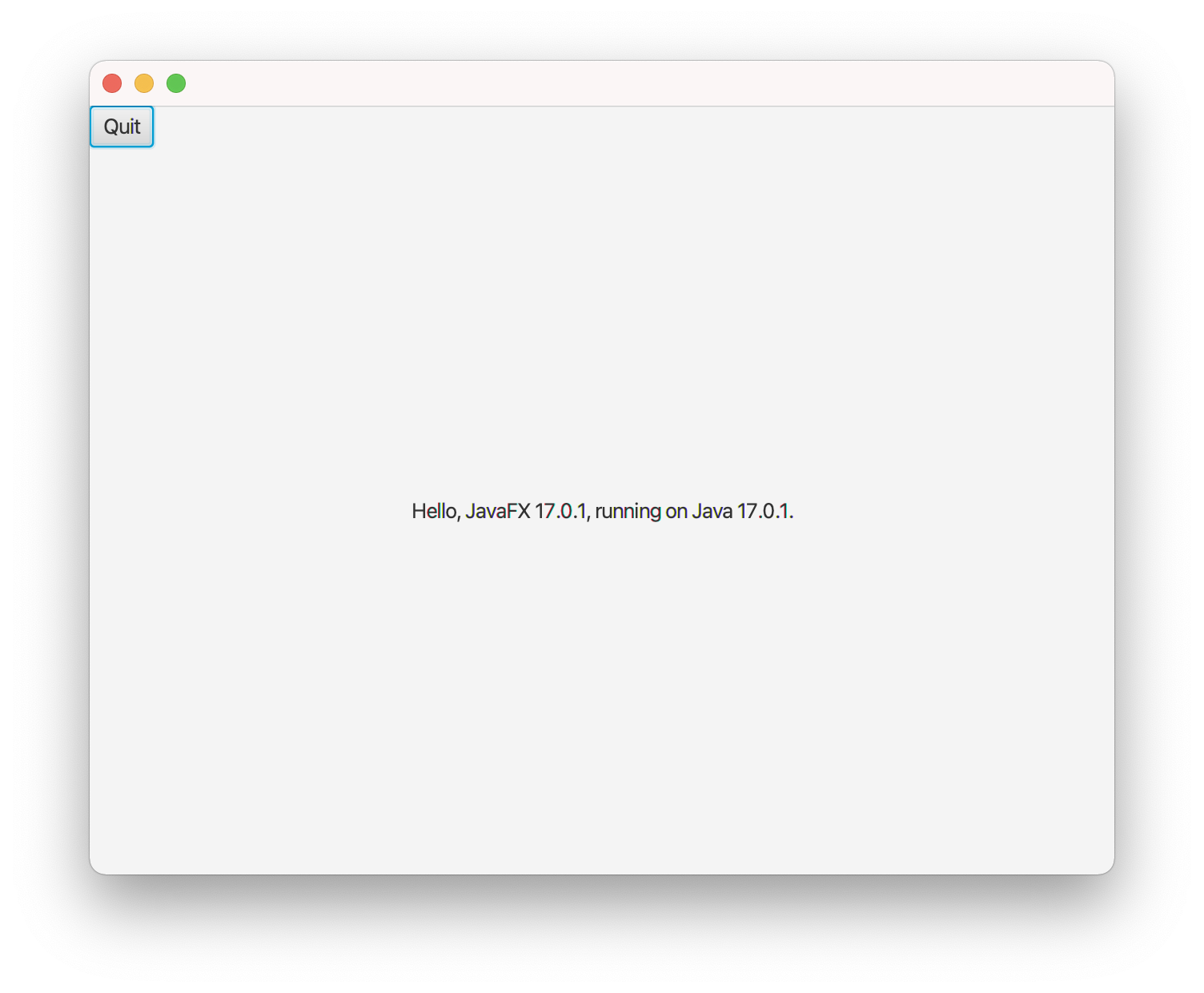
Complete instructions for installing JavaFX are here .
You can write a project in Java or Python. If you use Python, you are expected
to incorporate libraries and techniques that you haven't seen in class. You might
want to look into Numpy and
MatPlotLib.
You can obviate spreadsheets using Pandas.
You can install these with pip3
in a command window.
unix> pip3 install numpy unix> pip3 install matplotlib
Another popular option is to use pygame
Also there are web scraping and HTML parsing libraries
as well..
Inheritance and Interfaces
Types All interfaces and classes are types. All variabes in Java must have a type.
The type of a variable determines what methods are visible. This is the visibility principle.
When a method call is communicated via a variable, the "pointee" is responsible for executing the method. This is the delegation principle, so-called because the job of executing the code is delegated to the pointee.
Types in Java are organized into a hierarchy.
All classes automatically inherit from the root
class
java.lang.Object.
This is why any class you create automaticaly has
the methods toString() and equals.
final Again
So far the final keyword has appeared in
one context; variables marked final cannot be
reassigned. Finality is a property of variables and not
of objects.
The final keyword can appear in two
contexts in inheritance.
- If a class is marked
final, it cannot be extended. The classStringand the wrapper classes are all final classes. - If a method in a class is marked
final, it cannot be overrriden by a descendant class
Both of these stipuations are enforced at compile time. This article supplies a security rationale for making the String class final.
This will not compile. Try doing so and learn to recognize the error message that spits out.
public class APString extends String
{
}
Abstract Classes
Any class can be marked abstract; this prevents
any instances from being made of it using new.
Abstract classes exist for the sole purpose of being parent
classes. If a class is not abstract, it is said to be
concrete.
You can mark methods in a class abstract; if
you do, you end the header with a semicolon. Abstract methods
must be bodyless. A child class must override all abstract
methods in an abstract parent class.
Any class containing an abstract method must be marked abstract. Consider this class.
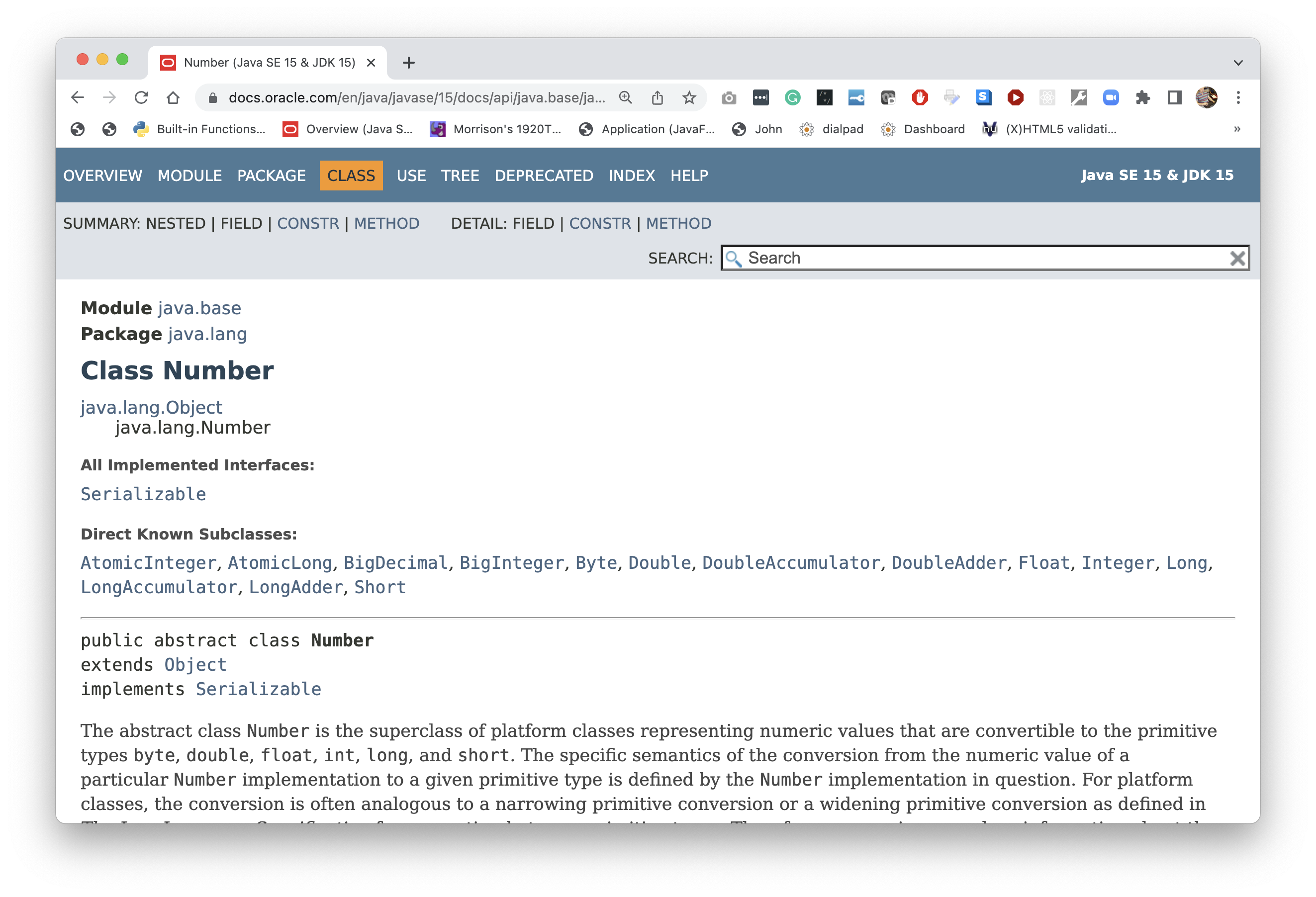
Just below the horizontal rule, you can see this class
is marked abstract.
jshell> Number n = new Number(5);
| Error:
| java.lang.Number is abstract; cannot be instantiated
| Number n = new Number(5);
| ^-----------^
jshell> Number n = 5;
n ==> 5
jshell> n.getClass()
$2 ==> class java.lang.Integer
You can see that you cannot create instances of
Number. However, since Number
is a type, you can have a variable of Number
type. Here we see we have created an Integer.
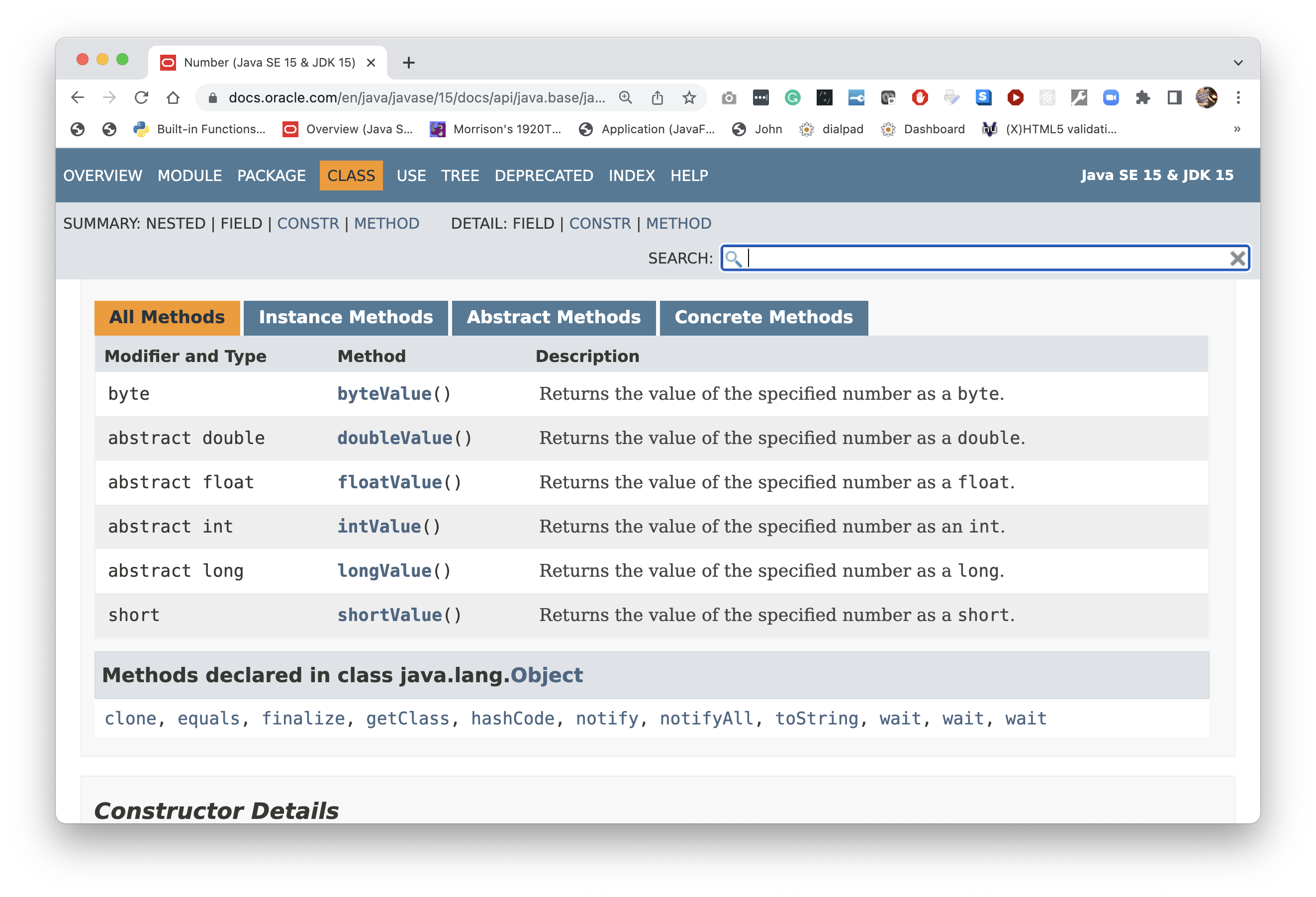
Notice that most of the methods here are marked
abstract. Also notice the flock of familiar
child classes.